According to the 1987 Brundtland Commission Report, the definition of sustainable development is “Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs”. Sustainability is considering the future by striking a balance between environmental, social and economic factors and the pursuit of improved quality of life.
Starting from 01 Jan 2016, all listed companies in Hong Kong are required to disclose their ESG information on an annual basis3. By integrating ESG into business strategies, the corporation would be able to mitigate the risks and benefit from transitional opportunities. Therefore, a corporation with better ESG performance tends to have more outstanding financial performance.
According to United Nation led initiative, the Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI), the following are examples of ESG issues:
Climate change – a defining challenge of our time. Different countries, regions and stakeholders are paying more attention to the adverse effects of climate change. One of the reasons causing climate changes is using fossil fuels in many human activities5, such as: power generation, transportation, industrial production and so on. These activities will increase the greenhouse gas concentration in the atmosphere which leads to global warming and deriving different environmental problems: change in precipitation, rise of sea level, loss of ecological and environmental balance and so on.
In order to solve or alleviate the problems caused by climate change, countries around the world are also committed to proposing different solutions:
The Paris Agreement came into force on 04 November 2016, the key provisions of the Paris Agreement call for global actions to:
- Keep global average temperature increase well below 2°C relative to pre-industrial levels and to pursue efforts to limit it to 1.5°C.
- Achieve ‘peak’ greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions as soon as possible and achieve a balance between carbon sources and sinks in the second half of the 21st century.
China’s nationally determined actions by 2030 include:
- To achieve the peaking of carbon dioxide emissions around 2030 and making best efforts to peak early
- To lower carbon dioxide emissions per unit of GDP by 60% to 65% from the 2005 level
- To increase the share of non-fossil fuels in primary energy consumption to around 20%
- To increase the forest stock volume by around 4.5 billion cubic meters on the 2005 level
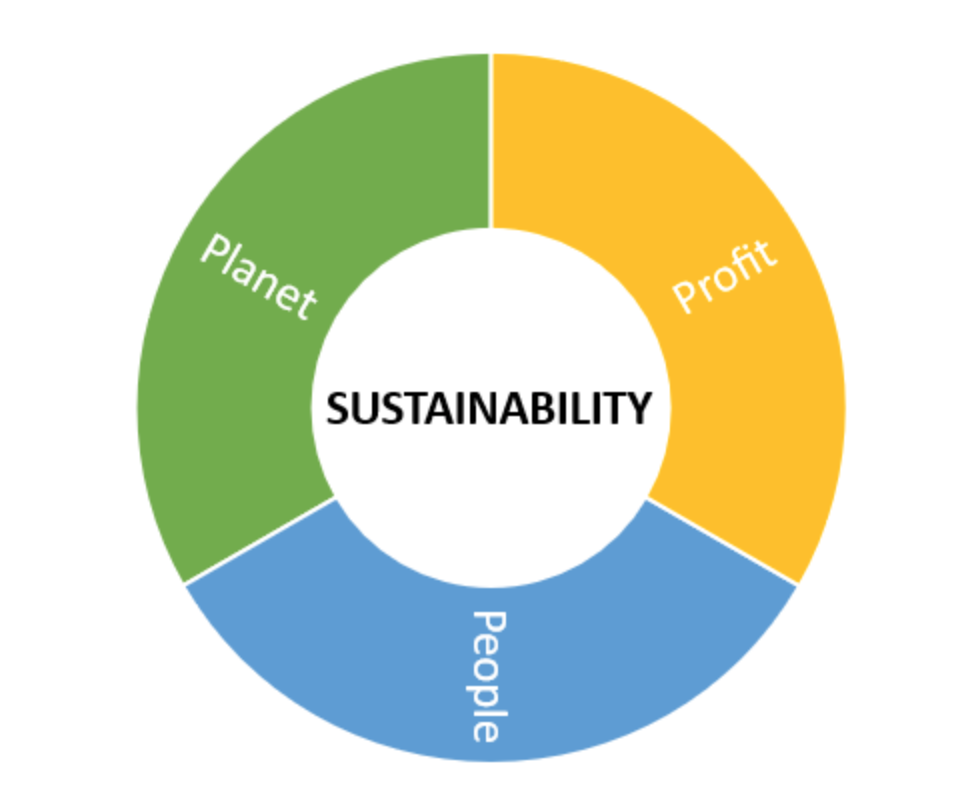

Investing in a corporation that has better ESG performance could provide you a long term and sustainable returns.
Today, many investors take into account ESG as a part of the investment decision making process.
Low-carbon investing is also an important aspect of ESG strategies as it can help to reduce the impacts of climate change risks and promote green technology.
Besides, the advantages of incorporating ESG into the business includes:
Companies with stronger ESG strategy can adapt necessary change and identify potential opportunities by capturing the market needs.
Check out the ESG Report of selected companies from 5 different industries: Logistics, Food & Beverage, Food Manufacturing, Environmental and Property Management.